Gum Graft Surgery: Types and Recovery Insights
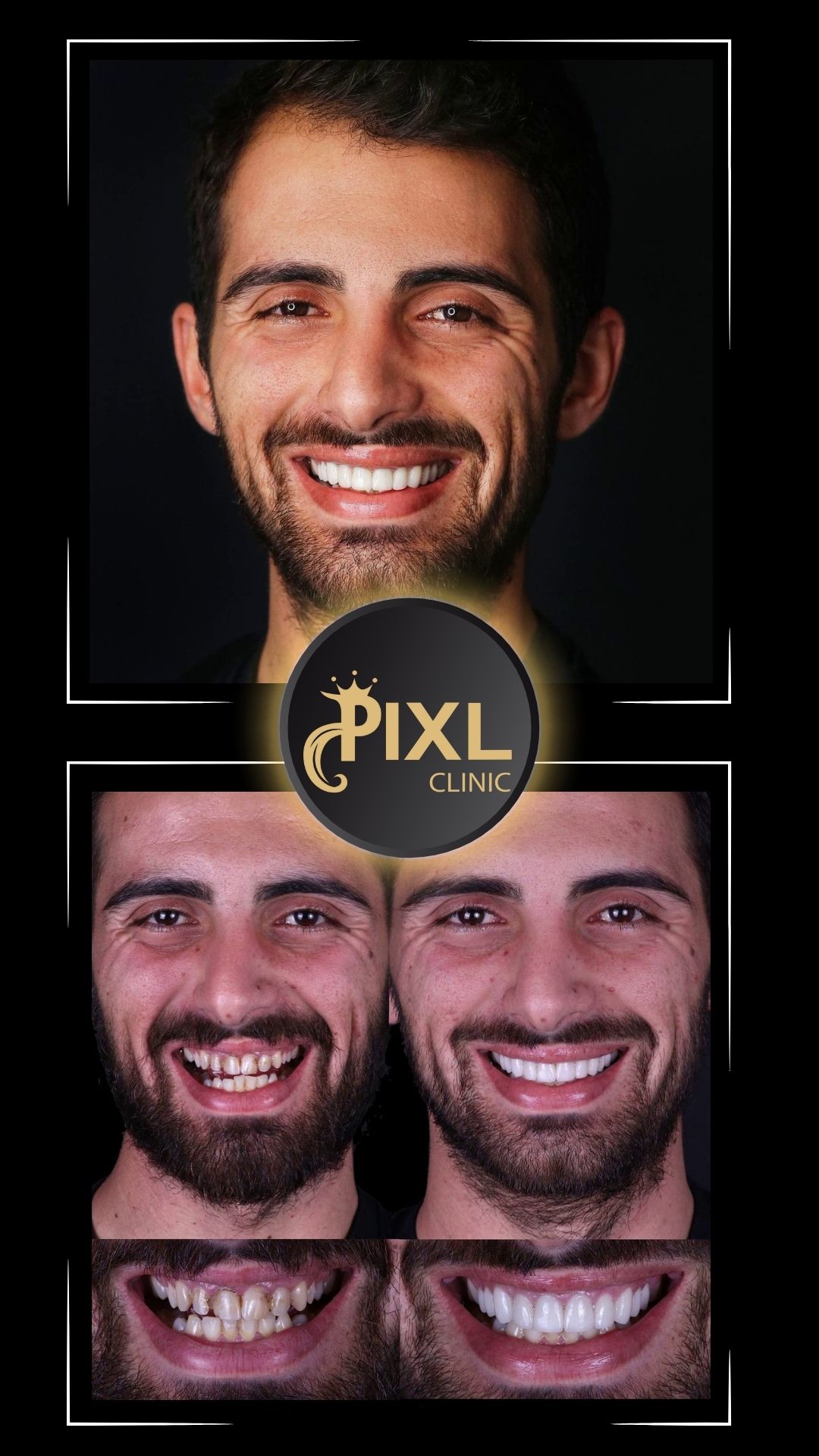
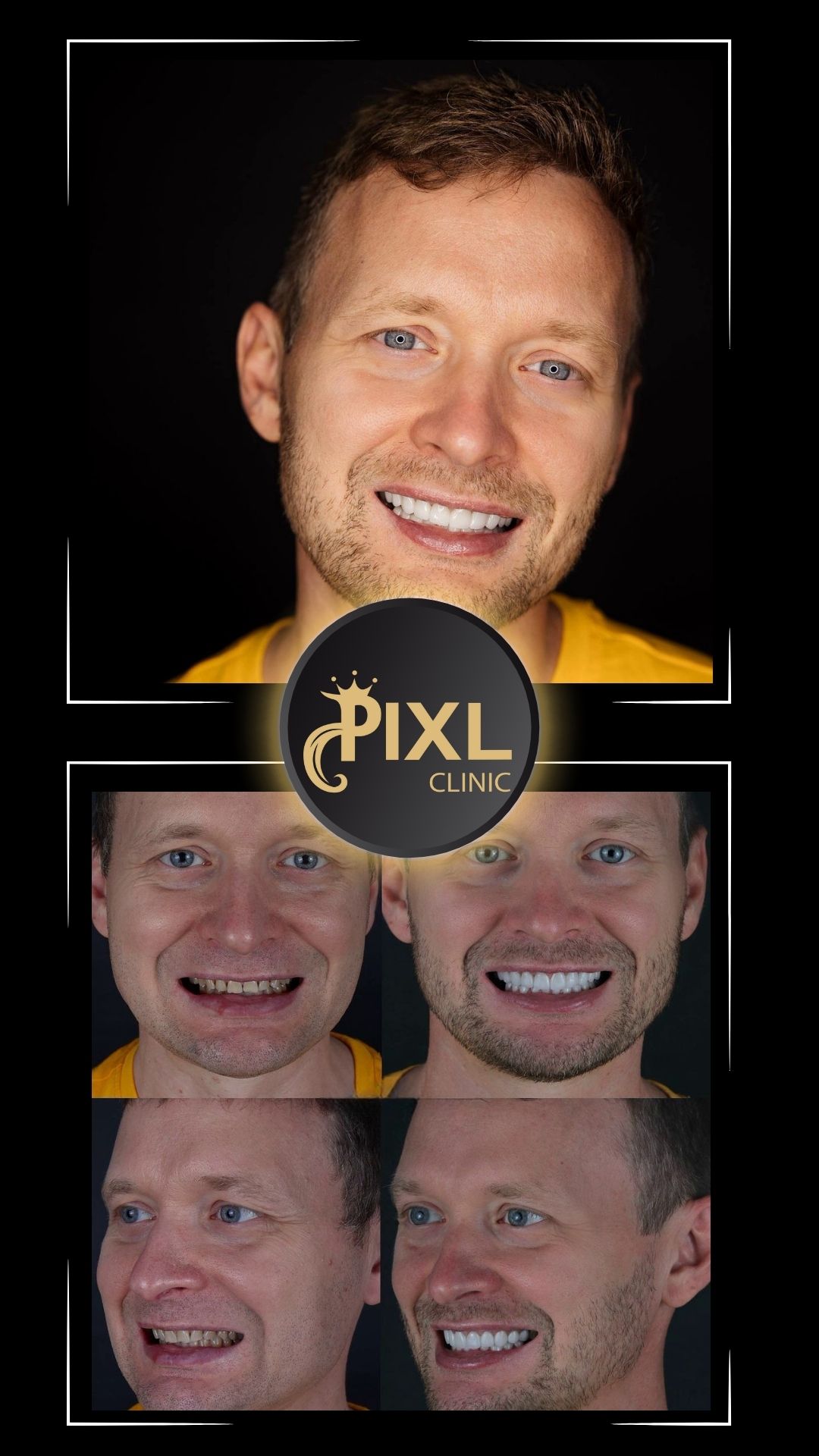
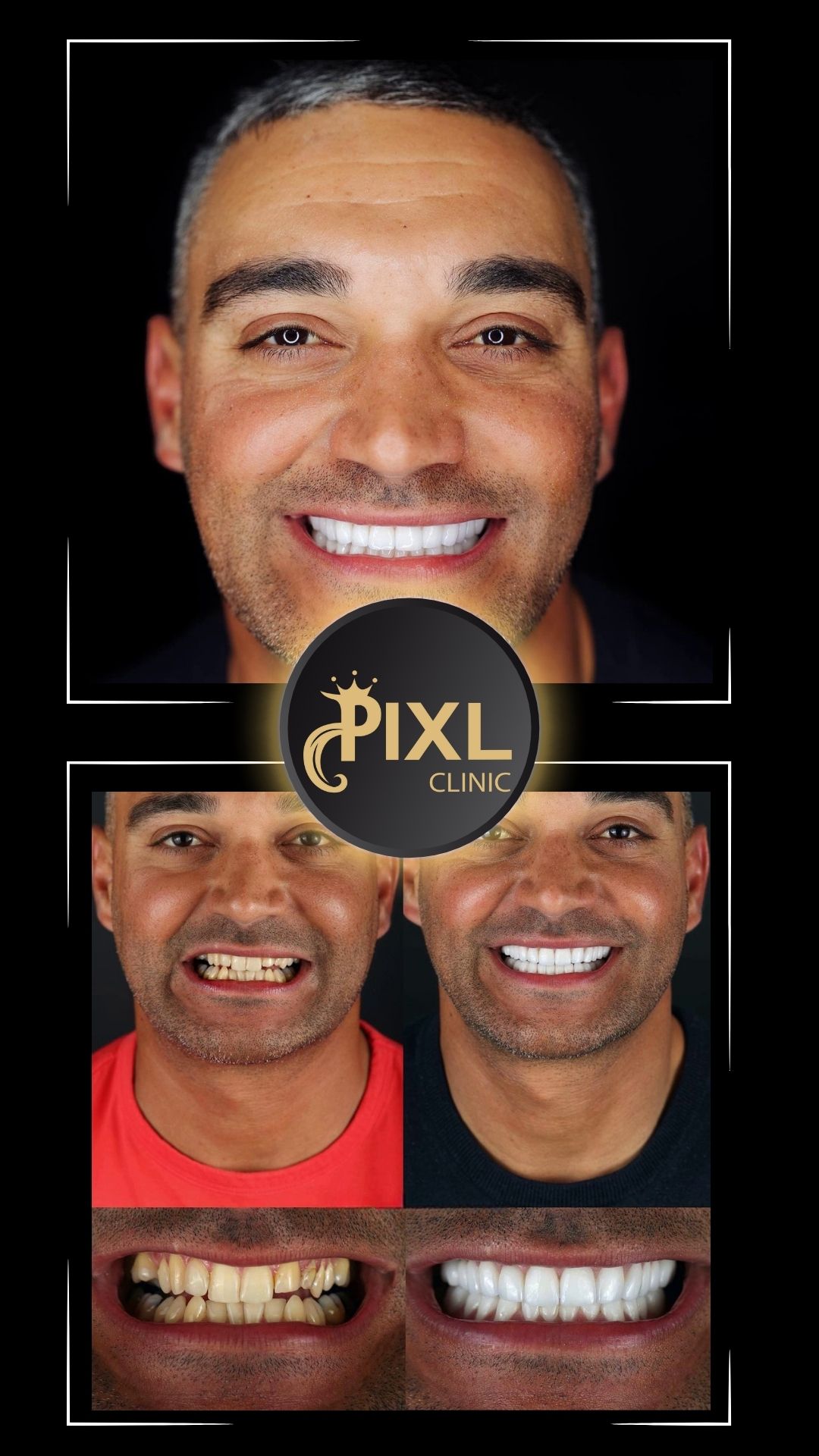
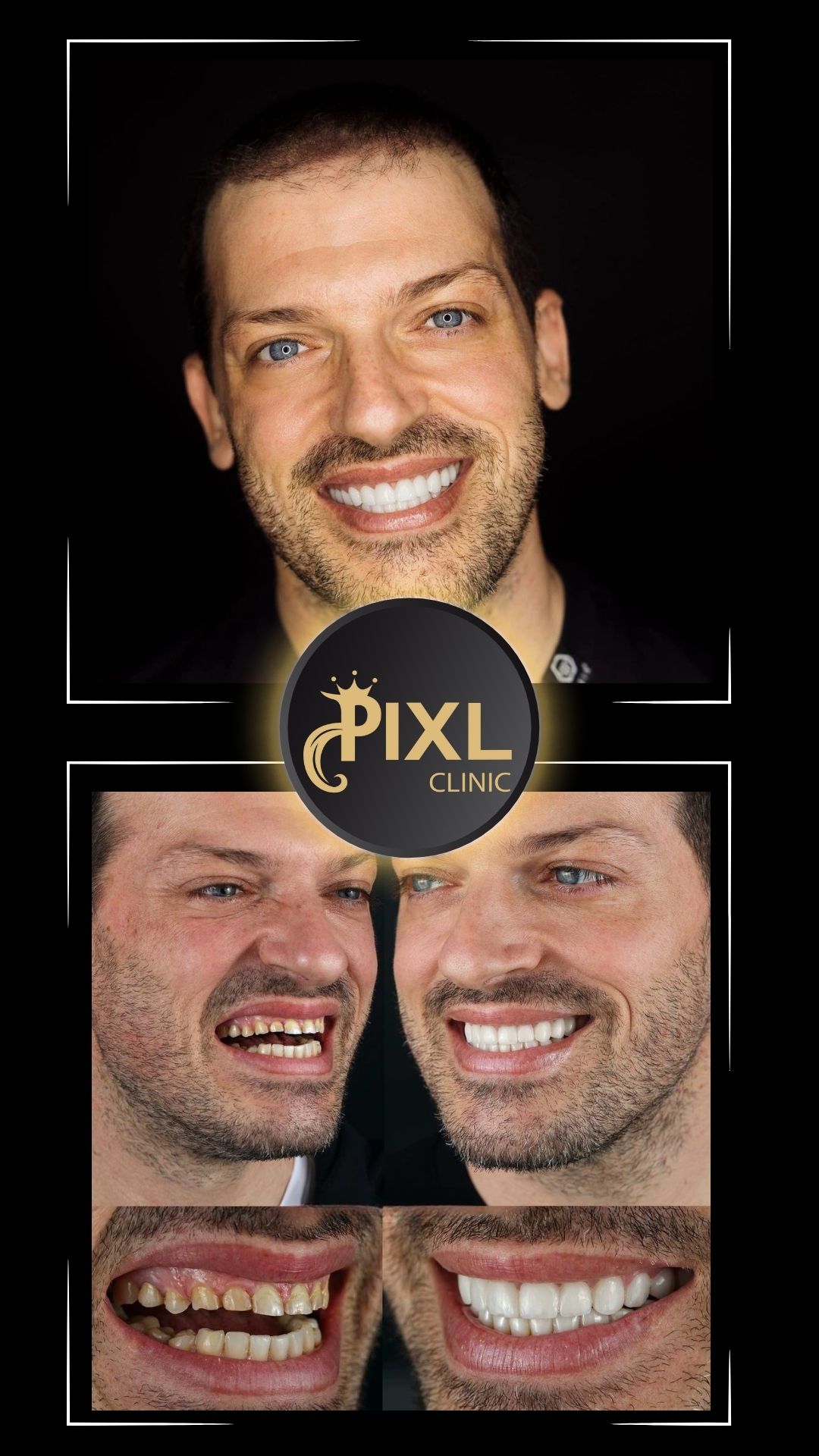
Gum health is a cornerstone of a radiant smile and overall oral health. For those experiencing gum recession, gum graft surgery can be a viable solution. This procedure restores gum tissue, protects teeth, and improves aesthetics. In this blog, we’ll explore the types of gum graft surgery, what to expect, and tips for a smooth recovery.
Understanding Gum Graft Surgery
Gum graft surgery is a dental procedure aimed at addressing gum recession, a condition where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls away, exposing the tooth root. This exposure can lead to increased sensitivity, decay, and potential tooth loss.
The primary goal of gum graft surgery is to regenerate lost gum tissue and cover exposed roots, protecting the teeth and enhancing the smile’s appearance. A periodontist typically performs this procedure, tailoring the approach based on the severity of the condition.
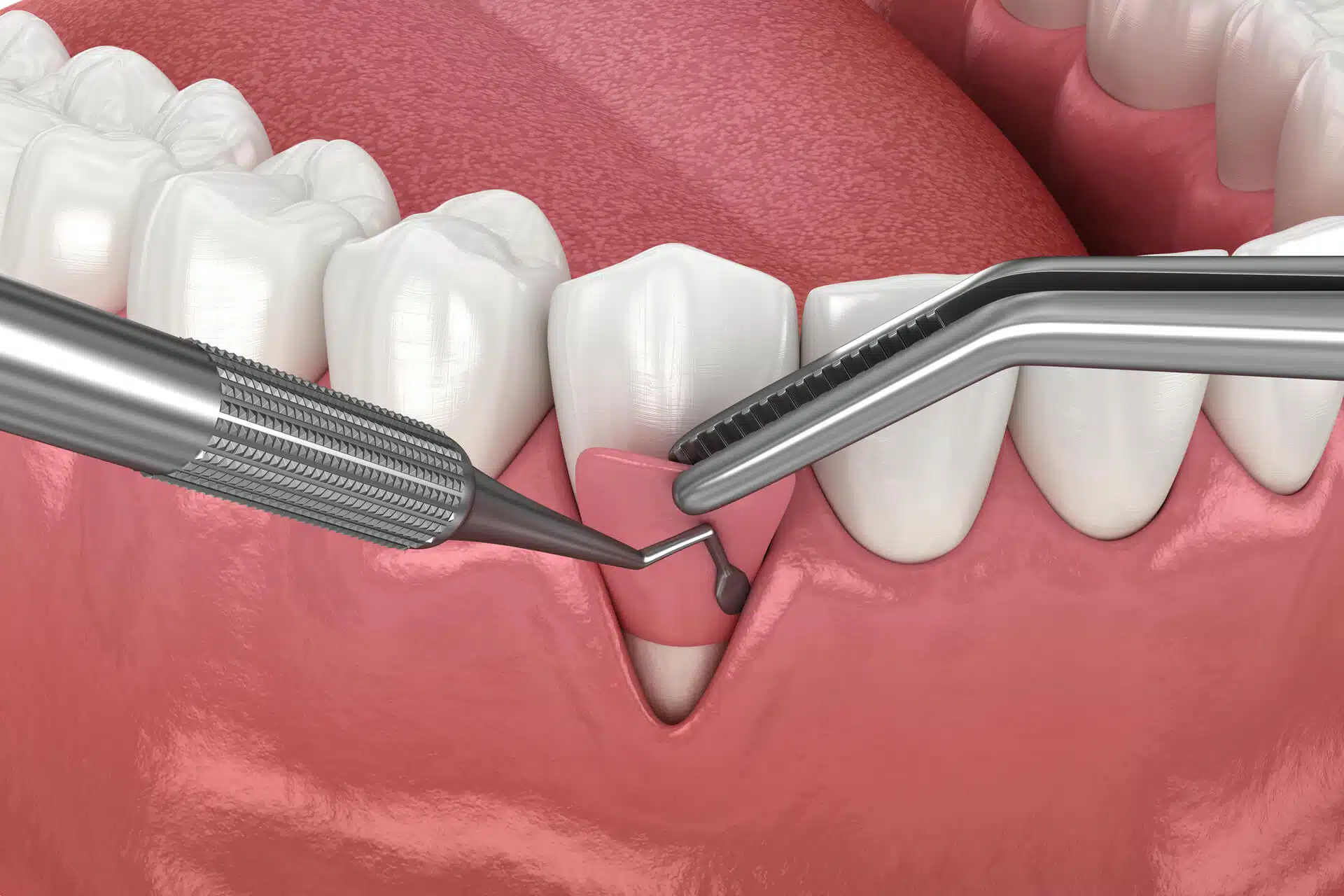
Types of Gum Graft Surgery
There are several types of gum graft surgeries, each suited to specific needs:
1. Connective Tissue Grafts
This is the most common type of gum graft surgery. It involves:
- Removing a small flap of tissue from the roof of the mouth (palate).
- Harvesting connective tissue from beneath the flap.
- Attaching the harvested tissue to the affected gum area.
Best for: Patients with significant root exposure or advanced gum recession.
2. Free Gingival Grafts
In this procedure:
- A thin layer of tissue is taken directly from the roof of the mouth.
- The tissue is transplanted to the gum area needing augmentation.
Best for: Patients with thin gums requiring reinforcement or minor gum recession.
3. Pedicle Grafts
This technique uses tissue from the gum near the affected area:
- A flap (pedicle) of tissue is partially cut and pulled over the exposed root.
- It remains attached to its original site to maintain blood supply.
Best for: Patients with adequate gum tissue near the recession site.
4. Allografts (Donor Tissue Grafts)
Instead of using the patient’s tissue, donor or synthetic tissue is employed:
- The material is grafted onto the affected area.
- This option eliminates the need for a second surgical site.
Best for: Patients who prefer less invasive options or have limited tissue available for harvesting.
What to Expect During the Procedure
Initial Consultation:
- The periodontist evaluates your gum health and determines the best graft type.
- X-rays or scans may be performed to assess underlying structures.
Day of Surgery:
- Local anesthesia is administered to numb the area.
- Tissue harvesting and grafting take place based on the chosen method.
- The surgery typically lasts 1-2 hours, depending on the complexity.
Post-Surgery Care:
- Sutures may be used to secure the graft in place.
- A protective dressing might be applied to shield the surgical site.
Recovery Insights
Recovering from gum graft surgery varies by individual and graft type, but understanding what to expect can ease the process.
1. Immediate Post-Surgery
- Discomfort: Mild pain or swelling is common and manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medication.
- Bleeding: Minimal bleeding may occur but typically subsides within a day.
2. Dietary Adjustments
- Stick to a soft-food diet for the first week to avoid disturbing the graft.
- Recommended foods include yogurt, mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs, and smoothies.
- Avoid spicy, crunchy, or hard foods that can irritate the surgical site.
3. Oral Hygiene
- Follow your dentist’s guidance on brushing and flossing around the graft area.
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to prevent infection.
- Avoid rinsing vigorously or using straws, which can dislodge the graft.
4. Activity Restrictions
- Limit strenuous activities for a few days to reduce the risk of bleeding or swelling.
- Rest adequately to aid healing.
Long-Term Care
After recovery, maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial to ensure the success of the graft and prevent further gum recession. Here are some tips:
- Brush gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Floss regularly to remove plaque without irritating the gums.
- Visit your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings.
- Consider wearing a night guard if you grind your teeth, as grinding can contribute to gum recession.
Benefits of Gum Graft Surgery
Gum graft surgery offers both functional and aesthetic benefits, including:
- Protection: Shields exposed roots from decay and sensitivity.
- Improved Appearance: Restores a natural, healthy gum line.
- Better Oral Health: Prevents further gum recession and associated issues.
Potential Risks and Complications
While gum graft surgery is generally safe, there are potential risks:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Graft failure or rejection.
- Prolonged swelling or discomfort.
Choosing a skilled periodontist and following post-operative care instructions significantly minimizes these risks.
Conclusion
Gum graft surgery is an effective way to restore gum health, protect your teeth, and enhance your smile. Whether you’re dealing with mild gum recession or more advanced cases, understanding the procedure and recovery process ensures a smoother experience.
If you’re considering gum graft surgery, consult with a qualified periodontist to determine the best course of action. With proper care and attention, you can look forward to a healthier smile and improved oral well-being.
Have you undergone gum graft surgery? Share your experience in the comments below, or let us know if you have any questions about the process!
Gum Graft Surgery FAQ
What is gum graft surgery?
Gum graft surgery is a dental procedure to restore receding gums by attaching new tissue to the affected area. It protects exposed tooth roots, improves aesthetics, and prevents further gum damage.
Why do I need gum graft surgery?
You may need gum graft surgery if you experience:
- Gum recession exposing the tooth roots.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages.
- Increased risk of tooth decay or loss.
- Cosmetic concerns due to uneven gum lines.
How do I know if I’m a candidate for gum graft surgery?
A periodontist will evaluate your gum health during a consultation. Candidates typically show signs of gum recession or have thin gum tissue that needs reinforcement.
What are the different types of gum graft surgery?
- Connective Tissue Grafts: The most common type, using tissue from the roof of your mouth.
- Free Gingival Grafts: Harvests surface tissue from the palate.
- Pedicle Grafts: Uses tissue from near the recession site.
- Allografts: Employs donor or synthetic tissue, avoiding a second surgical site.
Is the procedure painful?
The surgery is performed under local anesthesia, so you shouldn’t feel pain during the procedure. Some discomfort may occur during recovery, which can be managed with medication.
How long does the surgery take?
Gum graft surgery usually takes 1-2 hours, depending on the extent of the procedure and the number of teeth being treated.
What can I expect during recovery?
- First Few Days: Mild swelling, tenderness, and occasional bleeding are normal.
- Healing Time: Most patients recover in 1-2 weeks, but full healing of the graft may take several months.
What foods can I eat after surgery?
Stick to soft foods such as:
- Yogurt
- Mashed potatoes
- Scrambled eggs
- Smoothies Avoid crunchy, spicy, or hard foods that could disturb the graft.
Can I brush my teeth after the surgery?
Avoid brushing the surgical area initially. Use an antimicrobial mouthwash as directed by your dentist. Gradually resume gentle brushing once your periodontist approves.
Are there any risks or complications?
While rare, potential complications include:
- Infection at the graft site.
- Graft rejection.
- Prolonged swelling or discomfort. Following your dentist’s instructions reduces these risks.
How much does gum graft surgery cost?
The cost varies based on factors like the type of graft, extent of treatment, and your location. On average, prices range from $600 to $3,000 per tooth. Check with your insurance provider for coverage details.
Does insurance cover gum graft surgery?
Many dental insurance plans partially cover gum graft surgery, especially if it’s deemed medically necessary. Cosmetic procedures may not be covered.
How can I prevent gum recession in the future?
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene with regular brushing and flossing.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid irritating your gums.
- Avoid smoking, which contributes to gum disease.
- Attend routine dental cleanings and check-ups.
What if I don’t get gum graft surgery?
Untreated gum recession can lead to:
- Increased tooth sensitivity.
- Higher risk of cavities and decay.
- Tooth loss in severe cases.
- Worsening of gum health over time.
When can I return to normal activities?
You can typically resume light activities the day after surgery. Avoid strenuous exercise or heavy lifting for a few days to minimize bleeding or swelling.
How long does the graft last?
With proper care, gum grafts can last a lifetime. Maintaining good oral hygiene and attending regular dental check-ups are essential for long-term success.
































