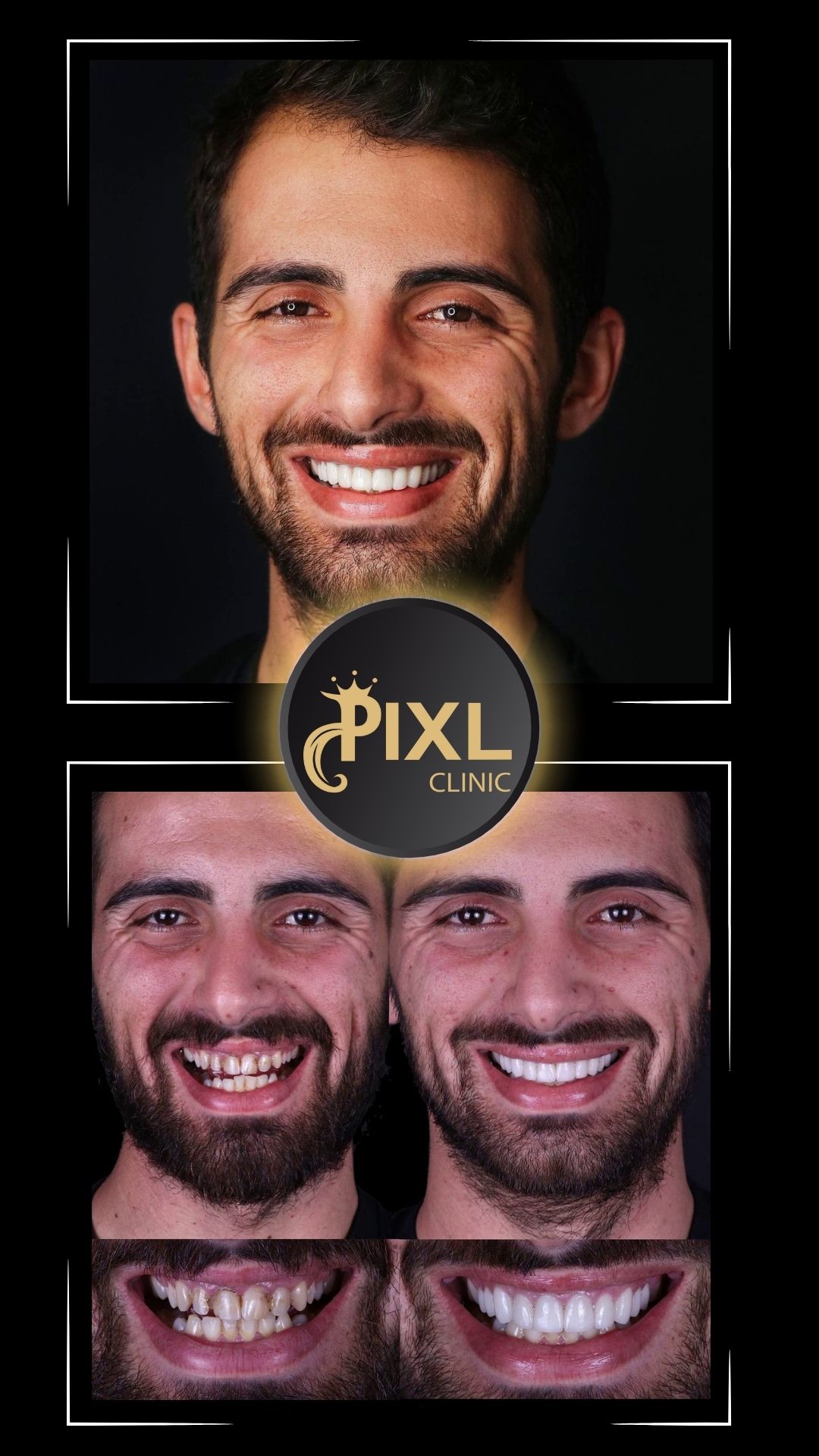
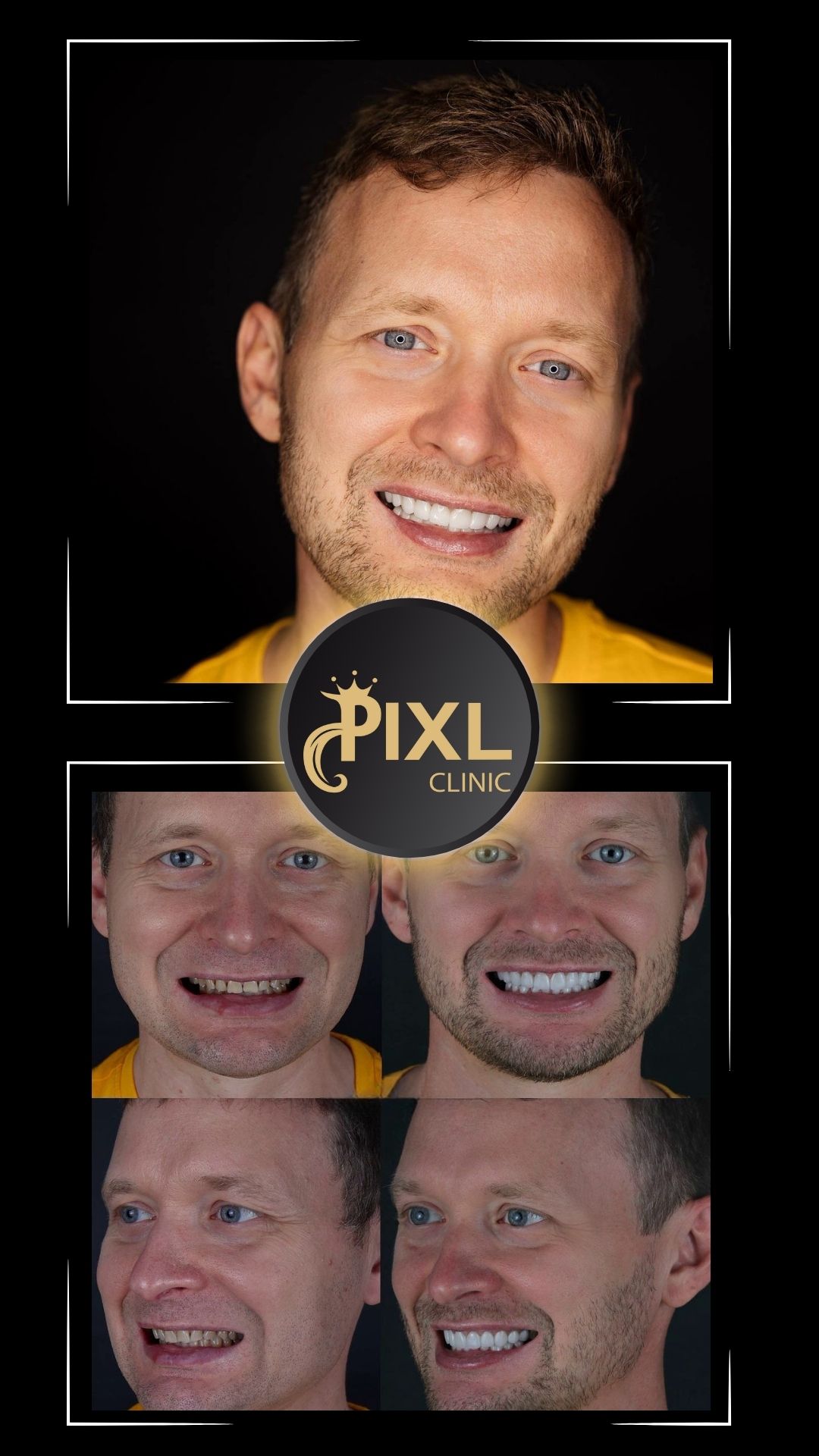
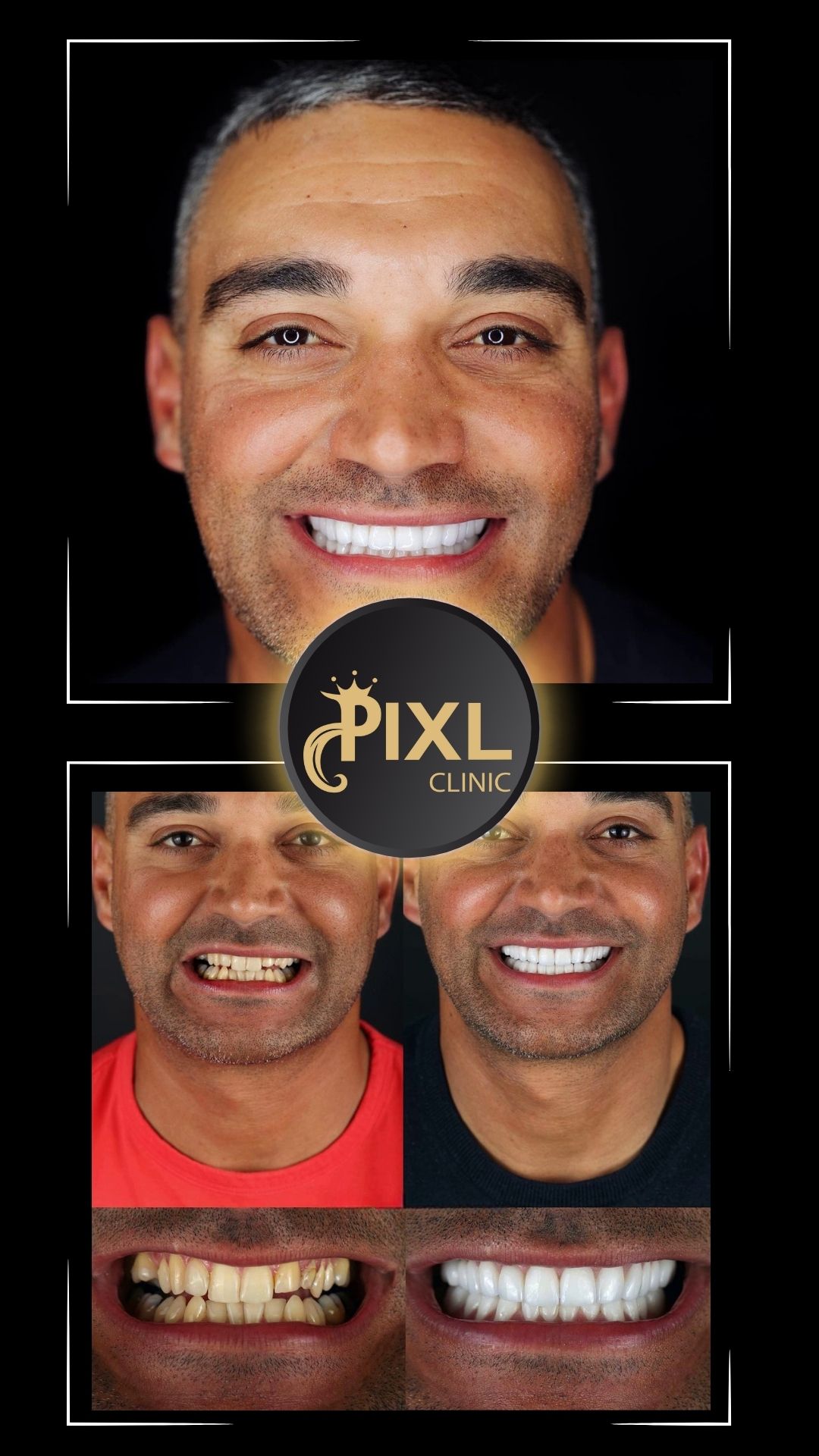
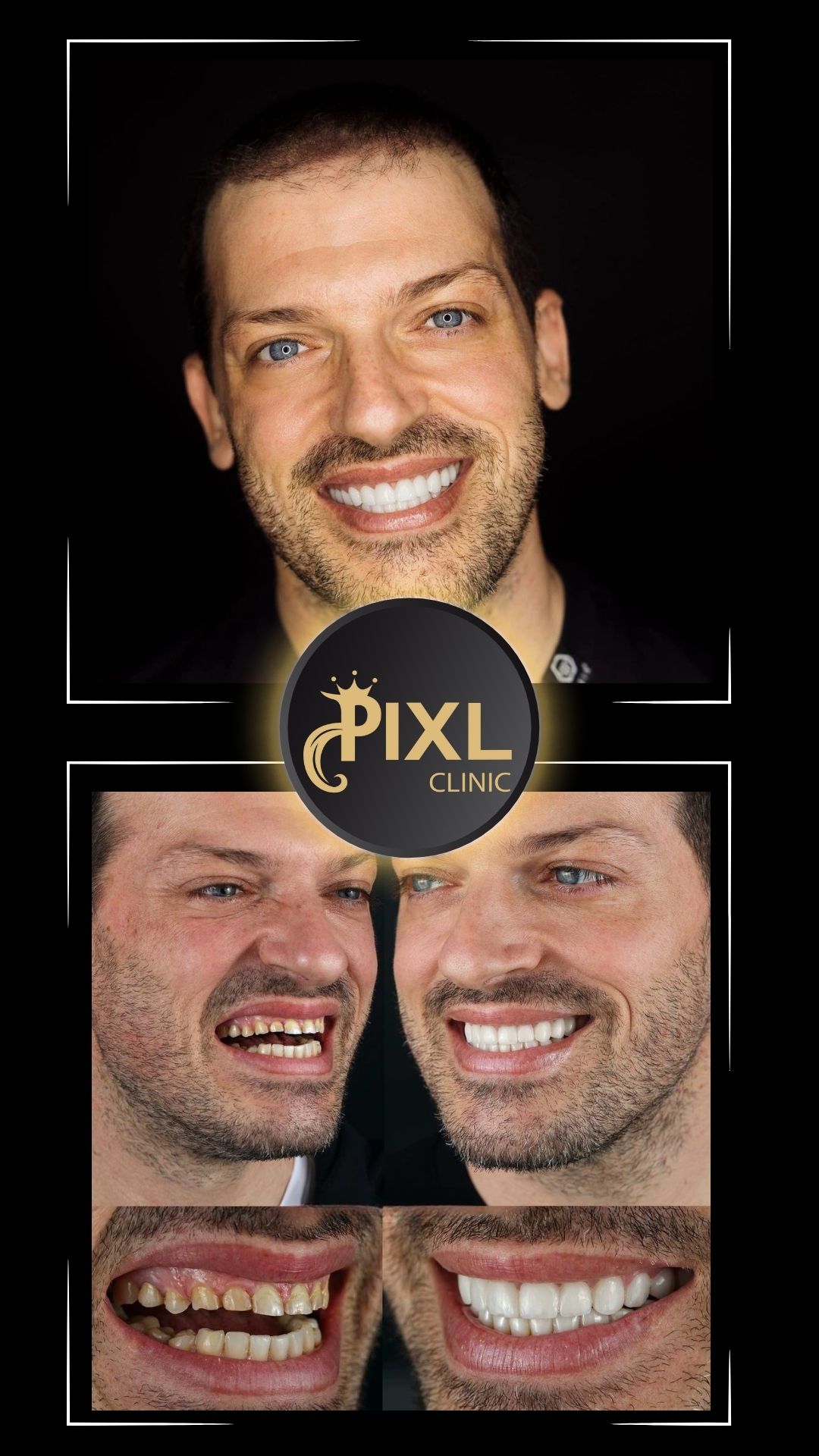
How to Know if You Have a Deep Bite and How to Treat It
A deep bite, also known as a deep overbite, is a dental condition where the upper front teeth excessively overlap the lower front teeth when the mouth is closed. While it may seem like a minor alignment issue, a deep bite can lead to discomfort, functional problems, and even long-term oral health complications if left untreated.
What Is a Deep Bite?
A deep bite occurs when the upper front teeth cover more than 30–40% of the lower front teeth when the jaws are closed. It is one of the most common forms of malocclusion (misaligned bite). This condition can range from mild to severe and may affect not only the teeth but also the jaw and surrounding structures.
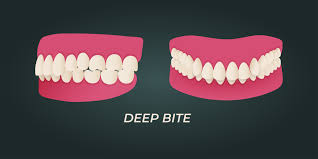
Signs and Symptoms of a Deep Bite
You may have a deep bite if you notice any of the following:
- Excessive Overlap: Your upper teeth cover a significant portion of your lower teeth when you close your mouth.
- Jaw Pain or TMJ Issues: A deep bite can cause strain on the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), leading to pain or discomfort.
- Tooth Wear: Excessive contact between upper and lower teeth may cause enamel wear, chipping, or cracking.
- Bite Marks on the Roof of the Mouth: Lower teeth pressing into the roof of the mouth may leave marks or cause irritation.
- Facial Pain or Headaches: Tension caused by the misalignment may lead to chronic facial pain or headaches.
- Speech Difficulties: Severe cases may interfere with proper tongue placement, affecting speech.
- Aesthetic Concerns: A deep bite can create an unbalanced facial profile or shorten the appearance of the lower face.
Causes of a Deep Bite
A deep bite can develop due to a variety of factors, including:
- Genetics: Family history of jaw or teeth misalignment.
- Jaw Growth Imbalance: Disproportionate growth of the upper or lower jaw.
- Overcrowded Teeth: Crowding can push teeth into misaligned positions.
- Tooth Loss: Missing teeth may cause adjacent teeth to shift and alter the bite.
- Teeth Grinding (Bruxism): Habitual grinding can wear down teeth, exacerbating the overlap.
- Poor Oral Habits: Thumb-sucking or tongue-thrusting in childhood can affect bite alignment.
How to Diagnose a Deep Bite
If you suspect you have a deep bite, it’s important to seek professional evaluation. Dentists and orthodontists use the following methods to diagnose the condition:
- Visual Examination: The overlap of your teeth will be assessed during a routine checkup.
- Dental X-Rays: Imaging helps determine the alignment of the teeth and jaws.
- Bite Analysis: Measures the severity of the overlap and how the teeth meet.
- 3D Imaging: Provides detailed insights into jaw alignment and bite issues.
Complications of an Untreated Deep Bite
Leaving a deep bite untreated can lead to the following issues:
- Severe Tooth Wear: Excessive contact can damage the enamel and increase sensitivity.
- Gum Recession: Misaligned teeth may press against the gums, leading to recession or gum disease.
- Jaw Pain and TMJ Disorders: Increased strain on the jaw joint may cause chronic pain or difficulty chewing.
- Speech Impairments: Severe cases can interfere with proper tongue movement and pronunciation.
- Aged Appearance: A deep bite can shorten the lower face, giving an aged or unbalanced look.
How to Treat a Deep Bite
The treatment for a deep bite depends on its severity and the patient’s age. Here are the most common options:
1. Braces
- How They Work: Traditional braces move teeth into proper alignment, reducing the overlap.
- Best For: Moderate to severe deep bites.
- Duration: 12–24 months, depending on the complexity.
2. Clear Aligners (e.g., Invisalign)
- How They Work: Removable, transparent aligners gradually reposition teeth.
- Best For: Mild to moderate cases in adults and teens.
- Duration: 6–18 months.
3. Bite Plates or Retainers
- How They Work: These devices prevent excessive contact between the teeth and encourage proper alignment.
- Best For: Mild cases or as a supplementary treatment to braces.
4. Orthognathic Surgery
- How It Works: Surgical correction of the jaw alignment may be required for severe cases.
- Best For: Adults with skeletal jaw issues causing the deep bite.
- Recovery Time: 6–12 weeks post-surgery.
5. Tooth Reshaping or Crown Lengthening
- How It Works: Modifying the length or shape of teeth can help correct minor alignment issues.
- Best For: Cosmetic improvements in mild cases.
6. Physiotherapy or TMJ Treatment
- How It Works: Jaw exercises or splints can relieve TMJ pain associated with a deep bite.
- Best For: Patients with jaw discomfort.
Preventing a Deep Bite
While genetics play a significant role in bite alignment, you can take steps to minimize the risk or progression of a deep bite:
- Early Orthodontic Evaluation: Have children evaluated by an orthodontist by age 7 to catch alignment issues early.
- Address Teeth Grinding: Use a night guard if bruxism is a contributing factor.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Healthy teeth and gums prevent complications associated with misalignment.
- Avoid Poor Habits: Thumb-sucking and tongue-thrusting should be corrected during childhood.
A deep bite is more than just a cosmetic concern—it can impact your oral health, comfort, and overall quality of life. Fortunately, modern orthodontic and surgical techniques can effectively correct this condition. If you suspect you have a deep bite, consult with a dentist or orthodontist to determine the severity and explore your treatment options.
With the right care, you can restore your bite, improve your oral health, and achieve a balanced, confident smile!
FAQs: Deep Bite and Its Treatment
What is a deep bite?
A deep bite, or deep overbite, is a dental condition where the upper front teeth significantly overlap the lower front teeth when the mouth is closed. This excessive overlap can cause functional, aesthetic, and health problems if left untreated.
How do I know if I have a deep bite?
Common signs of a deep bite include:
- Upper teeth covering most of the lower teeth when you bite down.
- Jaw pain or discomfort.
- Bite marks on the roof of your mouth from lower teeth.
- Excessive tooth wear or enamel chipping.
- Aesthetic concerns, like an uneven smile or altered facial profile.
What causes a deep bite?
A deep bite can be caused by:
- Genetics and jaw alignment issues.
- Teeth grinding (bruxism).
- Overcrowded teeth.
- Tooth loss, leading to changes in bite alignment.
- Habitual behaviors, such as tongue thrusting or chewing patterns.
Can a deep bite fix itself?
No, a deep bite will not resolve on its own. It typically requires orthodontic or surgical intervention, depending on the severity.
What are the complications of an untreated deep bite?
An untreated deep bite can lead to:
- Excessive tooth wear and enamel damage.
- Gum recession and increased risk of gum disease.
- Jaw pain and TMJ disorders.
- Speech and chewing difficulties.
- Aesthetic concerns, including an aged or unbalanced facial appearance.
What are the treatment options for a deep bite?
Common treatments include:
- Braces: Realign teeth and correct the bite over 12–24 months.
- Clear Aligners: Treat mild to moderate cases with discreet, removable trays.
- Bite Plates or Retainers: Prevent excessive tooth contact while encouraging alignment.
- Orthognathic Surgery: For severe cases caused by skeletal misalignment.
- Tooth Reshaping or Crown Lengthening: Address minor alignment issues.
How long does deep bite treatment take?
Treatment duration varies based on severity and method:
- Braces or aligners: 12–24 months.
- Surgery: 6–12 months, including recovery.
Can adults correct a deep bite?
Yes, adults can successfully treat a deep bite using braces, clear aligners, or surgery, depending on the complexity of the condition.
How much does deep bite treatment cost?
Costs vary based on the chosen treatment:
- Braces: $3,000–$8,000.
- Invisalign: $3,500–$7,000.
- Orthognathic Surgery: $10,000–$25,000.
Is a deep bite painful?
While a deep bite itself may not always cause pain, associated complications like jaw strain, headaches, or tooth wear can be uncomfortable. Treatment can alleviate these symptoms.
Are there non-invasive options to treat a deep bite?
Mild cases can be managed with bite plates or retainers, but moderate to severe deep bites often require orthodontic treatment or surgery for effective correction.
Can a deep bite cause speech problems?
Yes, severe deep bites can affect tongue placement, leading to speech difficulties such as lisping.
Can a deep bite lead to TMJ disorders?
Yes, misalignment caused by a deep bite can strain the jaw joint (TMJ), leading to pain, clicking, or discomfort.
How can I prevent a deep bite from worsening?
- Schedule early orthodontic evaluations for children (age 7+).
- Address habits like teeth grinding or tongue thrusting.
- Practice good oral hygiene to maintain tooth and gum health.
- Seek treatment for minor alignment issues before they progress.
When should I see a specialist for a deep bite?
If you notice excessive tooth overlap, jaw discomfort, or aesthetic concerns, consult a dentist or orthodontist for an evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and ensure a healthier smile.
































